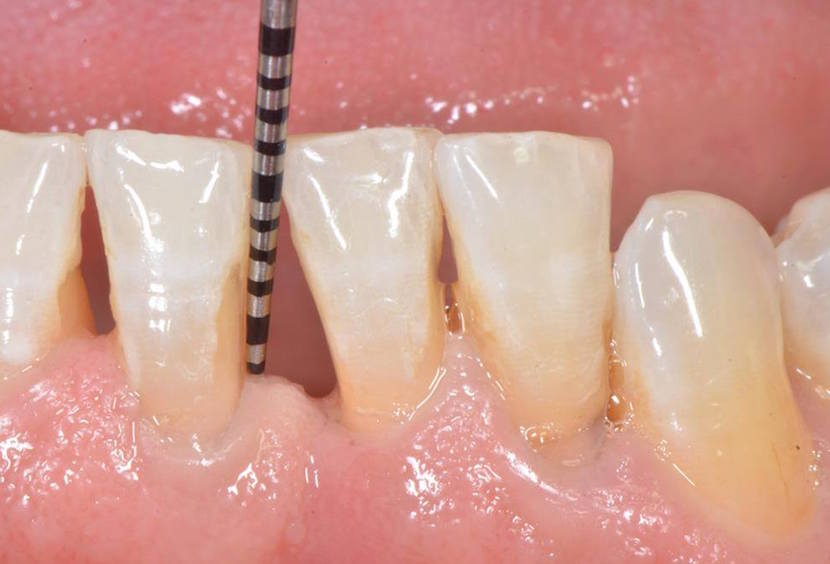
Tooth mobility is always an issue for patients who generally relate it with other pathologies such as periodontal diseases. There are, however, many other reasons that lead one or more dental elements to move; Let’s see which these reasons are and what to do in case of dental mobility.
Periodontitis
As the most recurring and feared pathology, the periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium, that is the whole tooth sustain structure, which, if not promptly treated leads to dental mobility and then to the loss of the dental elements involved by this pathology.
Behind this pathology, there is always the accumulation of bacterial plaque, which is in relation to the high or low individual sensibility to the periodontal disease. Plaque and tartar tend to accumulate by the gingival crevice especially because of an incorrect or low frequency teeth brushing with a possible consequence to expand to the gingival margin. Bacteria, here, can go undisturbed, creating the so-called gingival pocket and damaging the periodontium. This is the reason why it is necessary to keep an accurate home daily care within periodical dental hygiene session by professional dental office specialized in periodontology. This is remarkable because the standard dental hygiene usually keeps on the supragingival level without removing the subgingival tartar and plaque, which are the true responsible for periodontitis.
A clue to recognize a well done dental hygiene is the level of pain felt. The higher the pain is the better the hygiene have been done.
Unfortunately, there is no evident clue that helps us identifying the periodontitis; actually, the very first sign of a periodontal disease for a patient is often the dental mobility, which represents one of the last stages of the disease. The main reason why this pathology is often unnoticed is that the loss of bone, which is its peculiarity, does not necessary mean a gingival recession that is a gingival estrangement from the tooth. It is actually very common that the gingiva keeps being in its place although a moderate loss of bone. In this case, the gingival bleeding, due to the inflammation, represents a clear evidence of the disease, speaking of which the gingivae must never bleed.
Although the pathology is in place, there is still the chance to save the patient’s teeth and avoid the dental extraction and dental implantology.
It is important to know that the periodontist’s first step is oriented to the teeth preservation: instead of choosing surgery, it contemplates different dental hygiene sessions to remove the subgingival and the supragingival tartar. Our procedure, for example, contemplates the usage of sonic and ultra-sonic tools with whom the tartar croncretion from the tooth deep in the periodontal pocket helping to clean the radicular surface and allowing the periodontal tissues healing.
If periodontal pockets keep lasting, surgery is recommended.
Tooth Migration
The dental element migration occurs when a great quantity of bone has been lost due to the periodontitis and a high level of inflammation. The central incisors are generally those who move creating a space between the teeth. This migration can be partially reversible as the space between the teeth, which, can be partially or totally closed removing the subgingival tartar, that is removing the teeth inflammation. When a teeth migration is observed, it is important to contact your periodontist promptly because dental migration anticipates the dental elements loss if not intervening immediately.
Trauma
A trauma can also be the cause of dental mobility. It’s not so unusual for the tooth sustain structures to be damaged in order to cause dental mobility by a hit, a fall or any other accident. In any of these cases, never underestimate the damage and always let it check to your dentist who will surely value the situation finding out the best treatment for your problem.
Occlusal trauma
Occlusal trauma, known as the presence of excessive forces pushing on the teeth until damaging the periodontium, is another cause of dental mobility. Actually, these forces have such power to cause the dental mobility and then the loss of the tooth involved. As for the case of a tooth pre-contact or for the lack of molars there can occur an occlusal trauma leading to one or more teeth mobility. If promptly diagnosed, the occlusal trauma is completely reversible thanks to the simply removal of the pre-contact.
PREVENTION
As they say : “prevent is better than cure”, sponsored by a well know toothpaste brand, tells us a great truth connected to the dental mobility. No one should ever reach that moment where one or more teeth start to move, just because this could only mean that the teeth were already on their way for loss. Prevention is avoiding gingivae to recede without seeking for help so often and, most of all, it is avoiding that tartar accumulation during a long period of time could damage irremediably the gingivae.


Scrivi un commento: