WHEN
Dental checkups should start from the first year of age of the children.
HOW
Speed, communication and the right mood are fundamental in pedodontics.
WHY
To prevent cavities and analyze the development and growth of maxilla and mandible.
Paediatric dentistry (Pedodontics)
 Paediatric Dentistry (Pedodontics) is the branch of odontology that deals with the health of childrens’ and adolescents’ mouths. The Pedodontic aim is to educate the child and the parents to oral hygiene resources and eating habits to be adopted to prevent the onset of caries; but also to take care of teeth. The mental and physical approach is such, that it tries to overcome the fears of the young patient and it is characterized by dialogue and fast and non-invasive or painful procedures.
Paediatric Dentistry (Pedodontics) is the branch of odontology that deals with the health of childrens’ and adolescents’ mouths. The Pedodontic aim is to educate the child and the parents to oral hygiene resources and eating habits to be adopted to prevent the onset of caries; but also to take care of teeth. The mental and physical approach is such, that it tries to overcome the fears of the young patient and it is characterized by dialogue and fast and non-invasive or painful procedures.
It is often also important to cure milk teeth, even though they have got to be replaced with permanent teeth. Their destruction from caries or early loss in fact can cause more serious problems, such as deficiencies in the lining up of permanent teeth. As applicable, pedodontics therefore, belongs to all branches of dentistry, with the exception of osseointegrated implantology, since the positioning of osseointegrated implants is absolutely not recommended before the skeletal growth of patients is completed.
Infant dentistry also treats very small children thanks to an approach that seeks to establish collaborative and trusted relationships. The Pedodontist’s task is, first of all, to take care of prevention of caries and so motivate and teach the correct teeth brushing techniques, give suggestions about food diet and apply all prevention measures such as fluorine paints and sealants.
Also the Pedodontist’s job is to diagnose and treat some of the numerous disorders that damage the oral cavity, including caries, periodontal disease, and mineralization disorders, alterations of development and teeth eradication and traumatic injuries, even in special conditions such as those of children with handicap.
Deciduous teeth
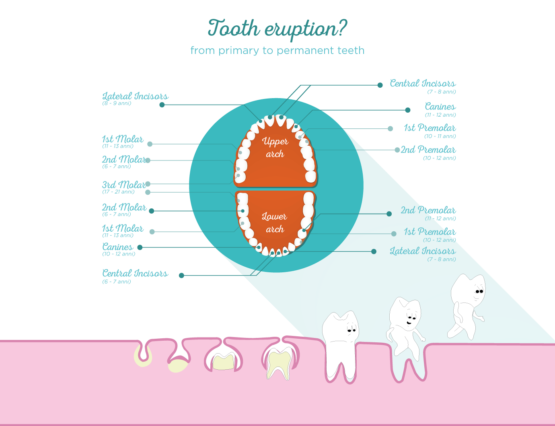
Every human being goes through a short phase of his life in which he has transition teeth called deciduous teeth, which will then, leave place for permanent teeth.
Deciduous teeth consist of 8 incisors that appear between 6-10 months (but this timescale may be wider), 4 canines (between 16-24 months), 4 first molars (between 12-20 months) and 4 second molars (between 24-30 months).
The child passes through a first exchange period, in which the milk incisors are replaced by permanent incisors, that is usually between 6 to 8 years and a second exchange period, in which milk canines and molars are replaced respectively by permanent canines and premolars. At the same time as the incisors fall, the first permanent molars appear, also called sixth. Often parents do not notice the eruption of this tooth because it does not replace any milk tooth, but erupts behind the last deciduous molar. To complete permanent dentition between 12-13 years permanent second molars erupt also called sevenths and third molars also called eighths around 18-25 years.
Contact us

When is the first dental appointment necessary?
The ideal would be that the pedodontist should look at the child from the age of 1. To take the first examination by the paediatric dentist early is important to build a good relationship between the child and the dentist which is based on trust and comfort for future examination. It is convenient that the first meeting of the child with the dentist does not coincide with the need to perform a treatment, which is when there is a toothache or when a trauma occurs, in order to avoid the impression that the dentist’s figure is linked to a negative experience.
Milk teeth should be treated even if they fall?
Milk teeth should always be looked after, since they perform important functions. They retain the space for subsequent permanent teeth, acting as guider in their eruption; are fundamental for the chewing and phonetics function; they allow a harmonious development of mandible and jaw; and in the end, they have an aesthetic function, helping to give a good image of them.
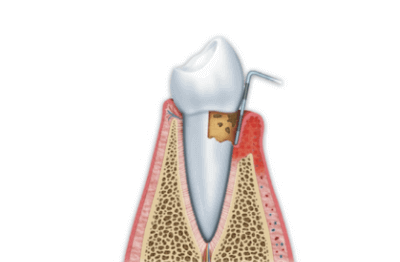
Therapies that are performed on milk teeth can be conservative care or endodontic care, depending on whether the carious lesion remains confined within dentin or interests the pulp chamber.

What to do in case of trauma?
Trauma is one of the reasons that most often bring children to dentist’s observation. Most of the injuries are caused by falls during recreational or sports activities.
There may be several occurrences due to the traumatic event; the most frequent are the fracture, the avulsion or the intrusion of the tooth element.
In the event of the crown fracture it is crucial to recover the fragment of the dental element, store it ap-propriately (physiological solution, milk or saliva) and go to a dentistry specialist immediately. He will, if possible, re-attach the fragment, restoring the integrity of the tooth.
In the case that the fracture involves the pulp of the dental element you will first proceed to the treatment of the endodontium (canal therapy or apicogenesis/apexification depending on whether the root of the tooth is completely or partially formed).
How to prevent tooth decay?
The first form of caries prevention is oral hygiene since the first tooth comes through, parents can use gauze. Then it is important to educate the child to use the toothbrush after each meal. It is also important that the child follows a correct feeding plan, limiting the consumption of very sugary foods (for example sweets, jam, and fruit juices) and avoiding categorically the use of sugars such as honey or fruit juices, especially when administered with a pacifier or a baby bottle.
The most powerful caries prevention measure is the topical fluoroprophylaxis. The use of fluoride toothpastes makes the tooth more resistant to the attack of caries acids. Instead, high-concentration fluoride products, such as gels or paints, can be applied professionally on deciduous and permanent teeth. The intake of fluoride by systemic means, in the form of tablets or drops, does not seem to be effective, as evidenced by the latest scientific evidence.
Finally in subjects at high risk of caries, it is possible to seal by composite resins, the chewing area of the molars, making it so smooth and easy to cleanse. This preventive method reduces the accumulation of plaque in the molars grooves and dimples, where children’s caries originates in most cases.